Adjectives are descriptive words like young, old, beautiful etc.
In German, adjectives change their endings depending on whether the person or thing you are referring to is masculine, feminine or neuter and whether singular or plural.
It also depends on the case/kasus of the person or thing you are describing and whether it’s preceded by the definite or indefinite article
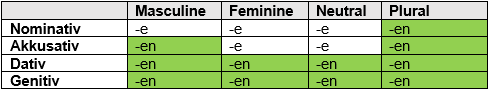
Adjectives used after the bestimte artikel / definite article (e.g. Der, Dierser. Welcher, Jeder, Mancher)
Example sentences:
| Nominative | Der junge Hund hat Hunger. (The young dog is hungry.) | Hund is Maskulin, Der Hund |
| Accusative | Ich habe die junge Katze gefüttert. (I’ve fed the young cat.) | Katze is Feminin Die Katze |
| Dative | Er hilft dem jungen Kind beim Anziehen. (He helps the young child to get dressed.) | Kind is Neutrum Das Kind |
| Genitive | Der Hund des jungen Mannes ist sehr krank. (The dog of the young man is very ill | Man ist Maskulin Der Man |
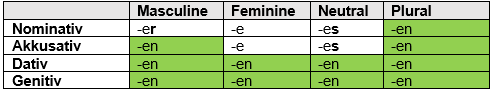
Adjectives used after the unbestimte artikel / indefinite article (e.g. Ein, Kein, Mein, Sein, Irgendein)
The Ein, Kein follows the same rules as the unbestimte artikel,
For Der Mann
Nominativ – Ein Junger Mann
Akkusativ – Einen Jungen Mann
Dativ – Einem Jungen Mann
Genitiv – Eines Jungen Mann
Example Sentences:
| Nominativ | Ein ehrgeiziger Fußballspieler trainiert täglich mehrere Stunden. | Fußballspieler is Muskulin |
| Akkusativ | Der Trainer beobachtet einen ehrgeizigen Fußballspieler. | Fußballspieler is Muskulin |
| Dativ | Ein Manager bietet einem ehrgeizigen Fußballspieler einen Profivertrag an. | Fußballspieler is Muskulin |
| Genitiv | Die Freundin eines ehrgeizigen Fußballspielers freut sich mit ihm. | Plural |
Adjectives used with no Article
When there is no Article, you “add” the artikel with the Adjective. The rules are mostly the same as for the Definite Article (The – Der, Die, Das). Genetiv is different for Masculine and Neutral, in stead of – des it is en
For Der Mann
Nominativ – Junger Mann
Akkusativ – Jungen Mann
Dativ – Jungem Mann
Genitiv – Jungen Mann

Example sentences:
| Nominative | Gute Freunde sind wichtig. (Good friends are important.) | Die Freunde |
| Accusative | Ich trinke gerne guten Wein (I like drinking good wine.) | Der Wein |
| Dative | Zu gutem Wein esse ich gerne Käse. (I like eating cheese with good wine.) | Der Wein |
| Genitive | Die Hilfe guter Menschen ist wichtig (The help of good people is important.) | Plural |



You must be logged in to post a comment.