Here is a short introduction to the structure of sentences. It will help you understand what is the difference between a subject, object, preposition, verb and articles
| English | German | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
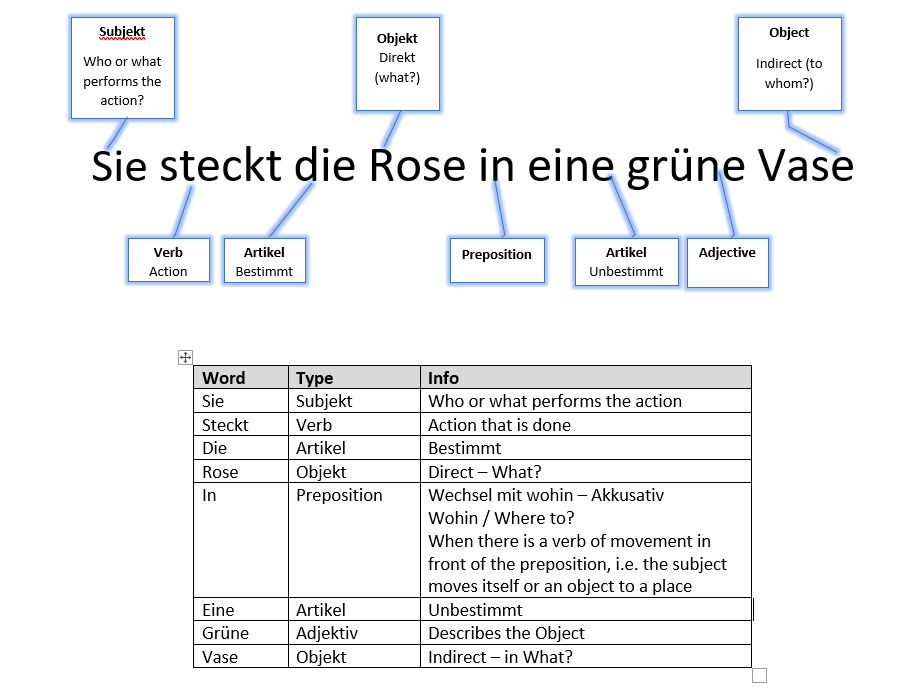
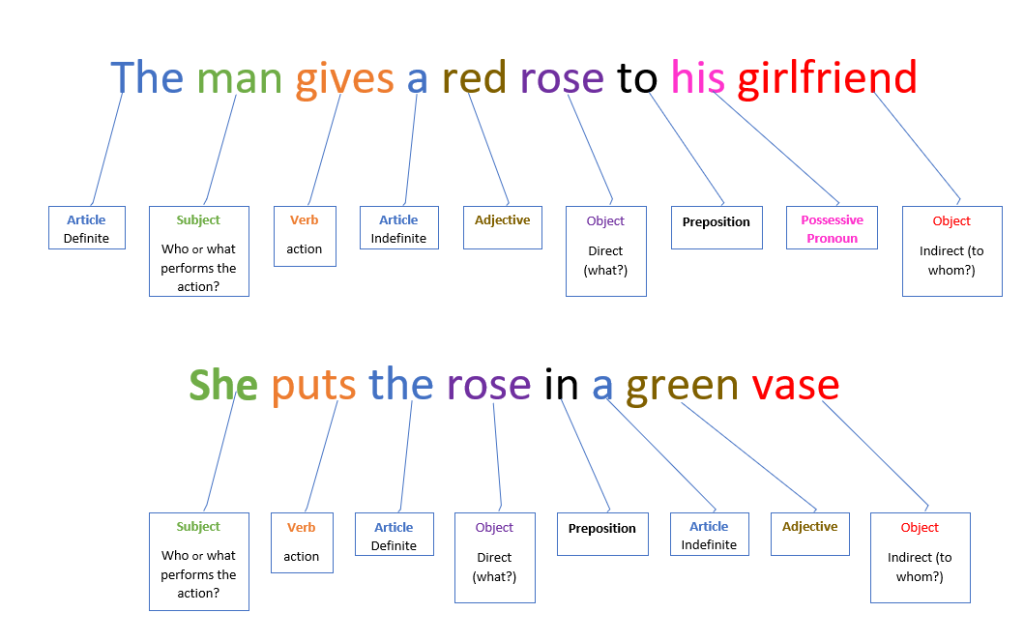
| Article | Artikel | Comes before a noun | Definite (Bestimmte) – The (Die Der Das) Indefinite (Unbestimmte) – a/an (Ein, Eine, Einen..) |
| Noun | Nomen | A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea | Car, house, girl Always capitalised in German Auto, Haus |
| Subject | Subjekt | Noun – The person or thing doing something | |
| Object | Objekt | Noun – Having something done to it | |
| Direct (Akkusativ) | The direct object is the receiver of the action A direct object answers the question “what?” or “who?” In German Wen? |
||
| Indirect (Dativ) | An indirect object answers the question “to whom?”, “for whom?” In German Wem? |
||
| Pronouns | Pronomen | A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun. | I, me, he, she, herself, you, it, that, they, each, few, many, who, whoever, whose, someone, everybody |
| Possessive Pronouns | Possessivpronomen | Words we use to show possession. | Mine, yours, his |
| Verb | Verb | Action | Eat, love, paint, write |
| Adjective | Adjektiv | Describes the Noun or Pronoun | Blue , big, clean, old. The young boy plays outside |
| Adverb | Adverb | An adverb describes a verb or anything apart from a noun and pronoun. How? When? How much? How often? E.g. how does the boy sing | The boy sings loudly |
| Prepositions | Präpositionen | A preposition is a word or set of words that indicates location | In, near, beside, on top of, behind. with |
Visual Grammar – German




You must be logged in to post a comment.