The German School system is quite unique and distinguishes itself from the South African models in a number of ways
| South Africa | Germany | |
|---|---|---|
| School Term | Starts in January | Starts in September |
| School Uniform | compulsory | Public schools do not require school uniforms |
| Home Schooling | Allowed | Not allowed, school attendance is compulsory |
| School Fees | Fees payable depending on income and school | Public schools are free of charge. Private schools charges fees |
| Primary School | Grade 1 to Grade 7 Compulsory from age 6 | Grade 1 to Grade 4 Compulsory from age 6 |
| Secondary School | Grade 8 to Grade 12. Compulsory up to Grade 10 | From Grade 5. See more info in the Secondary School section. Compulsory until the age of 15 for a Gymnasium, else 16 years |
Types of schools
There are different types of schools to choose from in Germany. The main system is Public schooling, but if
There are different types of schools to choose from in Germany. The German public school system is renowned for its comprehensive approach to education. Students from all backgrounds have access to free education.
Other options are:
- Montessori
- Waldorf schools, based on Rudolf Steiner’s anthroposophical human studies. They are state-approved or state recognised independent schools.
- Jenaplan-Schulen
- The Catholic church also runs many Schools.
- International schools in most big cities.
Finding a school
The local Bürgerampt should be able to provide you with information about schools in your region.
For international schools, you can use the following links to search
- Agis-schools (Association of German International Schools)
- International-schools-germany
Germany's education system
Article 7 of the Grundgesetz (Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany) states the following:
- The entire school system shall be under the supervision of the state.
- Parents and guardians shall have the right to decide whether children shall receive religious instruction.
- Religious instruction shall form part of the regular curriculum in state schools, with the exception of non-denominational schools. Without prejudice to the state’s right of supervision, religious instruction shall be given in accordance with the tenets of the religious community concerned. Teachers may not be obliged against their will to give religious instruction.
- The right to establish private schools shall be guaranteed. Private schools that serve as alternatives to state schools shall require the approval of the state and shall be subject to the laws of the Länder. Such approval shall be given when private schools are not inferior to the state schools in terms of their educational aims, their facilities or the professional training of their teaching staff and when segregation of pupils according to the means of their parents will not be encouraged thereby. Approval shall be withheld if the economic and legal position of the teaching staff is not adequately assured.
- A private elementary school shall be approved only if the education authority finds that it serves a special educational interest or if, on the application of parents or guardians, it is to be established as a denominational or interdenominational school or as a school based on a particular philosophy and no state elementary school of that type exists in the municipality.
- Preparatory schools shall remain abolished.
The School Stages
The German education system has 5 Stages.
| English | German | Information |
|---|---|---|
| Preschool | Kinderkrippen, Kindergarten | This is optional. The Landesjugendämper (Youth Welfare office) monitors children who are attending preschool. Children are monitored but achievements are not assessed |
| Primary School | Grundschule From 6 years of age Grades 1 to 4 | This is an obligatory stage. For most States the following applies: “When the school year begins, all children who have turned six by June 30 of the current calendar year are obliged to attend primary school. The same applies to children who have turned six by June 30 of the following calendar year and who have been registered by their legal guardians in elementary school.” Children automatically advance to the 2nd grade Children are graded from the 2nd grade. A school report is called a Zeugnis The grading system is from 1 (very good) to 6 (very poor) Pupils do not receive any certificates after finishing this Stage |
| Secondary School | Weiterführende Schulen Sekundarstufe 1 (lower level) or Sekundarstufe II (upper level) | This starts after the Primary stage and it comprises of a lower level (Sekundarstufe I) and upper level (Sekundarstufe II) Sekundarstufe I are for pupils between the ages of 10 and 16 and includes grades 5 – 7 to 9 – 10 The subject matter is very general and is meant to prepare pupils for Sekundarstufe II Sekundarstufe II are for pupils between the ages of 15 -16 or 18, who wants to qualify for university and already finished Sekundarstufe I |
| Tertiary | Hochschulausbildung, Teriärbildung | Universities, Technical univcersities, Educational colleges (Pädagogische Hochschulen) Universities of applied sciences (Fachhochschulen) Dual Studies (Berufsakademi) and Fachschulen |
| Further Education or continuing vocational training | Masters, Ph.D. |
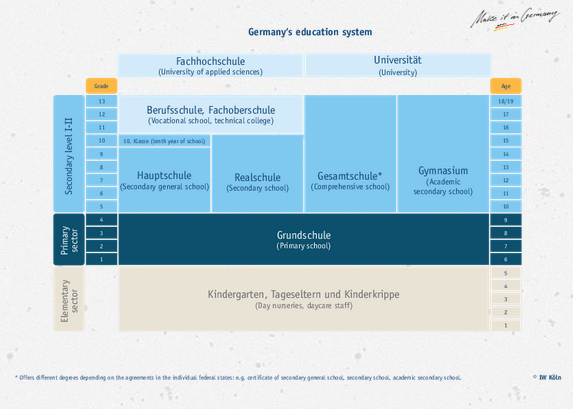
The Secondary School Stage
In Germany, the schools system sorts children into educational paths very early on and children have to make their future education choices at a young age. One major decision that parents and students will face is choosing the right secondary school. This choice will have a significant impact on a student’s academic and career opportunities, as well as their personal and social development. In Germany, there are several types of secondary schools to consider, each with different focuses and strengths. It is important to research and understand the curriculum, graduation requirements, and admission processes for each school in order to make an informed decision.
Each type of school caters to students with different academic abilities and career aspirations. The German school system also places a strong emphasis on vocational education and training. This ensures that students who prefer hands-on learning have plenty of opportunities to further their careers.
A South African Grade 12 could be equal to a German Abitur, depending on your subjects and marks (Note) and possibly the Bundesland. At a minimum, it should be equivalent to a Realschulabschluss/mittlere Reife.
To find out if your South African qualification allows you to study at a German University, enter your details on the Anabin Website
| English | German | Information |
|---|---|---|
| General school | Hauptschule (secondary general school for grades 5 through 9 or 10) | A secondary school in Germany and Austria, starting after 4 years of elementary schooling, which offers Lower Secondary Education (Level 2) according to the International Standard Classification of Education Students are eligible for vocational training afterwards, or can transfer to the Sekundarstufe II/Oberstufe at a Gymnasium or Gesamtschule. Pupils receive a Hauptschulabschluss certificate upon completion |
| General School – Practical | Realschule (practical secondary school for grades 5 through 10) | Students are eligible for vocational training afterwards, or can transfer to the Sekundarstufe II/Oberstufe at a Gymnasium or Gesamtschule. Another option is a FOS (Fachoberschule) There they can complete grades 11,12 and 13. You can enroll for Engineering at a Hochschule (University of Applied sciences) with FOS and Grade 12 Pupils receive a Realschulabschluss certificate upon completion |
| General School – Academic | Gymnasium (academic secondary school for grades 5 through 12 or 13) | Students receive an Abitur after successful completion and it entitles them to go to a University. Some degrees like Engineering, require up to grade 13. Students can also opt to do vocational training. |
| General School – Comprehensive | Gesamtschule (comprehensive school for grades 5 through 12 or 13) | Combines the Hauptschule, Realschule and Gymnasium and offers an alternative to the tripartite school system |
| Technical College (Vocational School) | Fachoberschule (FOS) | Pupils receive a graduation certificate or Mittlerer Schulabschluss meaning they will have a Fachhochschulreife. If the school offers grade 13, pupils will receive an Abitur or Fachgebundene Hochschulreife |
| Vocational Gymnasium | Berufliches Gymnasium | Offers 3 years of classes and pupils receive an Abitur upon completion |
Pupils are graded based on 6 marks:
- very good
- good
- satisfactory level
- adequate
- poor
- very poor.
Fun Facts
- On a child’s first day of school, they take along “Schultüte”, which is a decorated paper cone filled with sweets and small presents
- Depending on the Federal State, most children start school in August/September of the year that they turn 6 years old
- For young school children, having a trendy backpack is more important than the clothes they wear
- Every student is obliged to attend classes and other school events. You therefore cannot take your child out of school before the term ends. They must attend school for the whole term, with only certain exemptions like ill health, participation in sports competitions, or an important personal reason like the marriage of siblings, death in the family or serious illness in the family. Under certain circumstances, you can apply for special leave (Beurlaubung), for example, to return to your country of origin for a special event
- School hours start between 7:30 and 8:15 a.m. and can end between 12 noon and 1:30 p.m
- School marks are called “die Noten”
- A School hour is usually 45 minutes long
- Sports are played at private facilities and schools do not have sports fields
- At the end of an Abitur, most schools have Abiball which is like a Matric farewell
Information on the Web
- A really good article from Simple Germany
- Make-it-in-germany
- www.deutschland.de
- How to Germany (good definitions)
- School Terms
- Video from DW with relevant information
- pdf file in English with an excellent overview of the school system in Bavaria. This gives you a good idea about the school system and most states work on the same principles.
Related content

Recognition of studies
Depending on the situation, it might be necessary to have either your Matric/Grade 12 or South African degree or other qualifications and experience formally recognised

The German Vocational Training System
An Ausbildung is a form of vocational training or apprenticeship where a student attends school and works simultaneously. The student gains both theoretical and practical

Travel during a school Term
The school rules in Germany are very strict and every student is obliged to attend classes and other school events. You therefore cannot take your

Study in Germany
Types of learning institutions Hochschule is the name for higher education. Under this, you can get the following institutions. Fachhochschule – University of applied sciences.



You must be logged in to post a comment.